As you get older, you’re likely to notice visible signs of aging, especially in your skin and joints. Maybe playing your favorite sport isn’t as comfortable as it used to be or you’re seeing more fine lines and wrinkles in the mirror. While genetics, years of physical activity and lifestyle all play key roles in how and when signs of aging begin to show up, there is one crucial protein that affects everyone’s aging process: collagen.
Often referred to as the “fountain of youth,” or “holy grail of anti-aging,” collagen is a naturally occurring protein that not only supports the structure of your body but also contributes to your overall wellbeing. In this article, we will explore what collagen is, its importance to the human body and how it influences the aging process.
Understanding Collagen: The Basics
Collagen is the most abundant protein in the human body, making up around 30% of your total protein content. It provides structure to cells, acting as the building blocks for your skin, bones, tendons, ligaments and other connective tissues. Essentially, collagen provides strength, flexibility and resilience to these structures, ensuring their optimal functioning.
Understanding Collagen: Types of Collagens
There are several types of collagens found in the human body, but the majority are classified into three main types: Type I, Type II and Type III. Each type has a distinct role in maintaining the health and optimal function of specific tissues.
- TYPE I: Abundant in your bones and tendons, providing strength and elasticity.
- TYPE II: Predominantly found in cartilage, providing cushioning and support to joints.
- TYPE III: Present in the blood vessels and organs, contributing to their structural integrity.
When derived from external sources as a nutritional ingredient for collagen supplements, the key forms of commercially available collagen are classified by source and manufacturing process as follows:
- TYPE I: Hydrolyzed — Derived from porcine skin, bovine hide, eggshell membrane or fish, this collagen type is commonly sold as bone broth or collagen powder.
- TYPE II: Undenatured, unhydrolyzed collagen — Mostly derived from chickens.
- TYPE III: Hydrolyzed — Often derived from bovine sources.
- Vegan “collagen”: Genetically modified yeast and bacteria. Vegan “collagen” typically contains no collagen at all, but instead is formulated with collagen-boosting ingredients like vitamin C.
- Liquid BioCell®: A new generation of collagen, Liquid BioCell is a unique single-source matrix of hydrolyzed type II collagen + hyaluronic acid + chondroitin sulfate derived from chicken sternal cartilage in concentrations that mirror human articular cartilage concentrations.
The Importance of Collagen in Aging
As you age, your body’s production of collagen naturally declines, leading to visible signs of aging. This decline in collagen synthesis is influenced by various factors such as genetics, sun exposure, poor diet and environmental stressors, but eventually happens to everyone. What many people don’t realize is that collagen loss can start as early as your 20s. What’s more, collagen and the hormone estrogen are intrinsically linked, so when estrogen levels drastically drop during menopause, so does collagen.
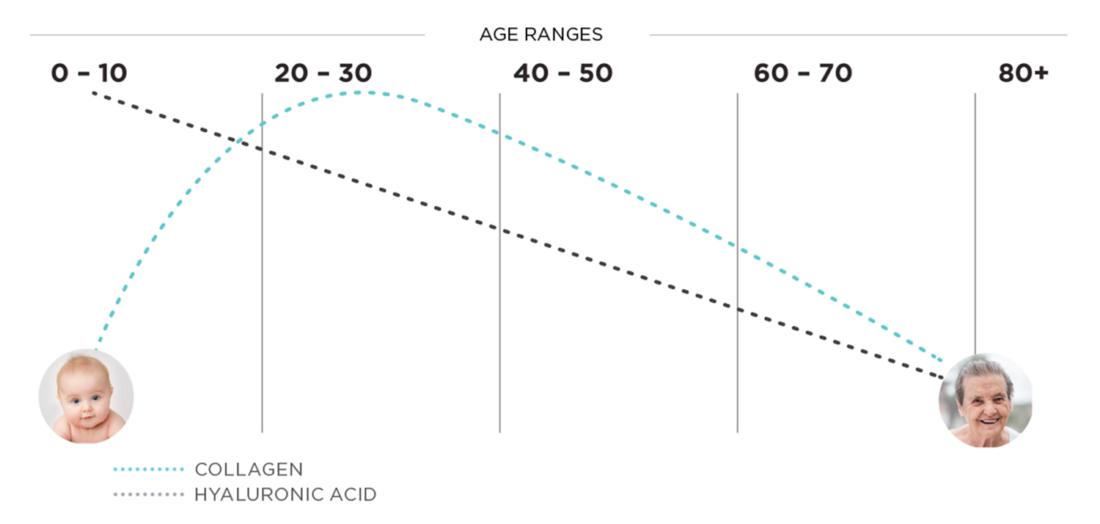
Here’s where collagen loss is most noticeable:
Skin Health
Collagen plays a vital role in maintaining the youthful appearance of your skin. It provides structure and elasticity, reducing the appearance of wrinkles, fine lines and sagging. Collagen levels directly impact your skin’s ability to retain its natural moisture barrier.
Joint Health
Collagen is a key component of cartilage, the cushioning material that covers your joints. It helps maintain joint flexibility and promotes comfortable joints to help you stay active.
Bone Strength
Collagen is responsible for the structural integrity of your bones, working in conjunction with minerals like calcium and phosphorus. Collagen levels can affect bone density and strength and may especially be essential for women in menopause and post-menopause.
Hair, Nails, Gums & Eyes
Collagen supports connective tissues that affect the healthy appearance of hair, nails and cuticles, your gums, and the fluid around your eyes. As collagen levels decline, it’s common to notice dry hair and hair breakage, as well as dry or brittle nails.
Ways to Support Collagen Production
While the natural decline of collagen cannot be completely prevented, there are steps you can take to support its production and change the way you age:
- Balanced Diet: Consuming a diet rich in protein, vitamin C and antioxidants helps promote collagen synthesis. Foods like lean meats, fish, fruits, vegetables and nuts can be beneficial.
- Sun Protection: Prolonged sun exposure can damage collagen fibers. Protecting your skin from harmful UV rays by wearing sunscreen, hats and seeking shade can minimize collagen breakdown.
- Lifestyle Choices: Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can help preserve collagen levels. Smoking accelerates collagen loss, while excessive alcohol can inhibit collagen production.
- Collagen Supplements: Collagen supplementation can help counteract the noticeable effects of collagen loss. However, not all collagen supplements deliver the benefits they may claim, so it’s important to seek out science-backed, studied formulas.
How to Choose a Collagen Supplement
If you’ve ever heard that ingestible collagen doesn’t provide any benefits, that’s partly true. In their natural state, collagen molecules are too large to be effectively absorbed by the body and are simply digested as proteins in the digestive system.
Hydrolysis is a process that breaks down these large collagen molecules for improved efficacy, so most supplements use hydrolyzed collagen. However, the method of hydrolyzation and the type and source of collagen used can yield widely varying results in the quality and effectiveness of the end product.
Formulated with multi-patented Collagen/HA Matrix® Technology, award-winning Liquid BioCell collagen is hydrolyzed using a patented Bio-Optimized™ manufacturing process to achieve an ideal micromolecule. The result is naturally enhanced bioavailability. Bioavailability has a direct bearing on how beneficial a supplement is because it measures how efficiently a substance enters a body’s circulatory system. That’s why merely ingesting a nutrient is not enough; it must be absorbed to derive any nutritional benefit.*
Liquid BioCell consists of type II hydrolyzed collagen, a major component of healthy joints, youthful skin and connective tissue; hyaluronic acid (HA) essential to skin hydration, tissue maintenance and a youthful appearance; and chondroitin sulfate to support joint flexibility and lubrication.*
Regardless of which collagen supplement you choose, make sure it’s backed by scientific research. The independent research on Liquid BioCell is conducted via multiple double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled human clinical trials and is third-party validated. These criteria are universally considered the highest standard for clinical studies in the scientific community.
Collagen is a fundamental protein that plays a crucial role in maintaining the youthfulness and vitality of your body. While aging is inevitable, understanding the significance of collagen and implementing strategies to support its production can help slow down the visible signs of aging. By nurturing your collagen levels through proper nutrition, sun protection, healthy lifestyle choices and evidence-backed collagen supplements, you can empower yourself to change the way you age.*
| *These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. These products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease. |









